You are given two integer arrays nums1 and nums2, sorted in non-decreasing order, and two integers m and n, representing the number of elements in nums1 and nums2 respectively.
Merge nums1 and nums2 into a single array sorted in non-decreasing order.
The final sorted array should not be returned by the function, but instead be stored inside the array nums1. To accommodate this, nums1 has a length of m + n, where the first m elements denote the elements that should be merged, and the last n elements are set to 0 and should be ignored. nums2 has a length of n.
Example 1:
Input: nums1 = [1,2,3,0,0,0], m = 3, nums2 = [2,5,6], n = 3
Output: [1,2,2,3,5,6]
Explanation: The arrays we are merging are [1,2,3] and [2,5,6].
The result of the merge is [1,2,2,3,5,6] with the underlined elements coming from nums1.
Example 2:
Input: nums1 = [1], m = 1, nums2 = [], n = 0
Output: [1]
Explanation: The arrays we are merging are [1] and [].
The result of the merge is [1].
Example 3:
Input: nums1 = [0], m = 0, nums2 = [1], n = 1
Output: [1]
Explanation: The arrays we are merging are [] and [1].
The result of the merge is [1].
Note that because m = 0, there are no elements in nums1. The 0 is only there to ensure the merge result can fit in nums1.
Constraints:
- nums1.length == m + n
- nums2.length == n
- 0 <= m, n <= 200
- 1 <= m + n <= 200
- -109 <= nums1[i], nums2[j] <= 109
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
class Solution {
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(int n1 : nums1){
if(n1 != 0)
list.add(n1);
}
for(int n2 : nums2){
if(n2 !=0)
list.add(n2);
}
int sub = m + n - list.size();
int sum = m+n;
if (list.size() < sum) {
for (int i = 0; i < sub; i++)
list.add(0);
}
Collections.sort(list);
int i=0;
for(int ans: list){
nums1[i] = ans;
i++;
}
}
}내 풀이!

import java.util.Arrays;
class Solution {
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
nums1[i+m]=nums2[i];
}
Arrays.sort(nums1);
}
}이해 쉽고 빠른 코드
의문은 int[] nums1은 배열인데
배열은 저장공간을 늘리거나 줄일 수 없다.
아..
문제를 다시 보니 int[] nums1의 저장공간은 이미 nums2의 길이만큼 확보된 문제였다.
문제를 더 잘 파악한 후 잘 고민해 봤다면 나도 이 방법으로 풀지 않았을까 싶다.
class Solution {
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
int k = m-1, j = n-1, r = n+m-1;
//begin from end
while(k >=0 && j >= 0){
if(nums1[k] > nums2[j]){//put it in last free pos from end
nums1[r--] = nums1[k--];
}
else {
nums1[r--] = nums2[j--];
}
}
while(r >= 0 && j >= 0){
nums1[r--] = nums2[j--];
}
}
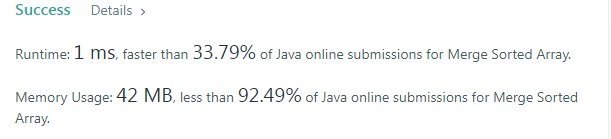
}빠른 코드
아직은 직접 떠올리기 어려워만 보이는 코드다.
'codingTest > LeetCode' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [LeetCode] 83 - Remove Duplicates from Sorted List (0) | 2022.03.31 |
|---|

댓글